5 8 13 21 34
The Fibonacci numbers are the numbers in the following integer sequence.
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, viii, xiii, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, ……..
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
Fnorthward = Fn-1 + Fn-two
with seed values
F0 = 0 and F1 = 1.
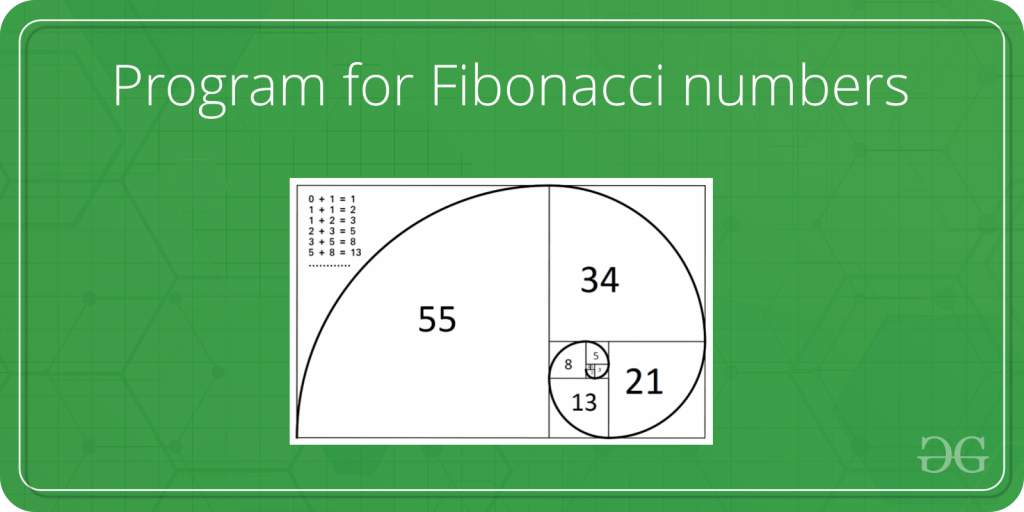
Given a number n, print n-th Fibonacci Number.
Examples:
Input : n = 2 Output : ane Input : n = 9 Output : 34
Write a function int fib(int northward) that returns Fdue north. For instance, if n = 0, then fib() should return 0. If n = 1, then it should return ane. For n > ane, it should render Fn-ane + Fnorth-2
For north = 9 Output:34
The following are different methods to become the nth Fibonacci number.
Method one (Use recursion)
A simple method that is a straight recursive implementation mathematical recurrence relation is given above.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fib( int n)
{
if (n <= one)
render due north;
render fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main()
{
int north = 9;
cout << fib(n);
getchar ();
return 0;
}
C
#include <stdio.h>
int fib( int northward)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(north - i) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main()
{
int due north = 9;
printf ( "%d" , fib(north));
getchar ();
render 0;
}
Java
class fibonacci {
static int fib( int n)
{
if (north <= i )
return north;
return fib(n - 1 ) + fib(due north - ii );
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int northward = 9 ;
Organisation.out.println(fib(due north));
}
}
Python3
def fibonacci(northward):
if northward < = 1 :
return n
render fibonacci(n - 1 ) + fibonacci(northward - ii )
if __name__ = = "__main__" :
n = 9
print (fibonacci(n))
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
public static int Fib( int due north)
{
if (n <= ane)
{
render n;
}
else
{
return Fib(n - 1) + Fib(n - 2);
}
}
public static void Main( string [] args)
{
int north = ix;
Console.Write(Fib(northward));
}
}
PHP
<?php
function fib( $n )
{
if ( $n <= 1)
return $n ;
return fib( $n - 1) +
fib( $n - 2);
}
$n = nine;
echo fib( $n );
?>
Javascript
<script>
permit n = 9;
function fib(north) {
if (n <= one)
return north;
render fib(due north-1) + fib(n-2);
}
certificate.write(fib(northward));
</script>
Time Complication: Exponential, as every function calls two other functions.
If the original recursion tree were to be implemented then this would take been the tree but now for n times the recursion part is called
Original tree for recursion
fib(5) / \ fib(iv) fib(3) / \ / \ fib(3) fib(ii) fib(two) fib(1) / \ / \ / \ fib(2) fib(1) fib(1) fib(0) fib(1) fib(0) / \ fib(1) fib(0)
Optimized tree for recursion for code above
fib(5)
fib(four)
fib(3)
fib(2)
fib(1)
Extra Space: O(n) if we consider the part call stack size, otherwise O(1).
Method two: (Use Dynamic Programming)
We can avert the repeated work done in method one by storing the Fibonacci numbers calculated and so far.
C++
#include<$.25/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class GFG{
public :
int fib( int northward)
{
int f[northward + ii];
int i;
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = i;
for (i = 2; i <= northward; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[due north];
}
};
int main ()
{
GFG thou;
int n = 9;
cout << g.fib(due north);
return 0;
}
C
#include<stdio.h>
int fib( int north)
{
int f[northward+two];
int i;
f[0] = 0;
f[ane] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= northward; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-two];
}
render f[n];
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf ( "%d" , fib(n));
getchar ();
return 0;
}
Coffee
public class fibonacci
{
static int fib( int n)
{
int f[] = new int [n+ 2 ];
int i;
f[ 0 ] = 0 ;
f[ 1 ] = 1 ;
for (i = 2 ; i <= northward; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i- 1 ] + f[i- ii ];
}
return f[n];
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9 ;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
};
Python3
def fibonacci(n):
f = [ 0 , 1 ]
for i in range ( 2 , north + ane ):
f.append(f[i - 1 ] + f[i - ii ])
return f[north]
print (fibonacci( 9 ))
C#
using System;
class fibonacci {
static int fib( int n)
{
int []f = new int [n + ii];
int i;
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = two; i <= n; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - two];
}
return f[n];
}
public static void Main ()
{
int n = ix;
Console.WriteLine(fib(northward));
}
}
PHP
<?php
function fib( $northward )
{
$f = array ();
$i ;
$f [0] = 0;
$f [1] = i;
for ( $i = 2; $i <= $due north ; $i ++)
{
$f [ $i ] = $f [ $i -one] + $f [ $i -two];
}
return $f [ $n ];
}
$n = 9;
echo fib( $northward );
?>
Javascript
<script>
part fib(n)
{
allow f = new Array(n+two);
let i;
f[0] = 0;
f[i] = one;
for (i = ii; i <= northward; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[north];
}
let northward=9;
certificate.write(fib(n));
</script>
Time complexity: O(n) for given n
Auxiliary space: O(north)
Method 3: (Space Optimized Method ii)
Nosotros tin can optimize the space used in method ii by storing the previous two numbers only because that is all we need to get the next Fibonacci number in series.
C++
#include<$.25/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fib( int n)
{
int a = 0, b = i, c, i;
if ( n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= due north; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
return 0;
}
C
#include<stdio.h>
int fib( int n)
{
int a = 0, b = i, c, i;
if ( n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= due north; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf ( "%d" , fib(northward));
getchar ();
return 0;
}
Java
public form fibonacci
{
static int fib( int n)
{
int a = 0 , b = ane , c;
if (n == 0 )
render a;
for ( int i = two ; i <= due north; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
public static void main (Cord args[])
{
int n = nine ;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
};
Python3
def fibonacci(n):
a = 0
b = 1
if n < 0 :
print ( "Incorrect input" )
elif due north = = 0 :
render a
elif due north = = 1 :
return b
else :
for i in range ( ii ,north + 1 ):
c = a + b
a = b
b = c
return b
print (fibonacci( 9 ))
C#
using System;
namespace Fib
{
public class GFG
{
static int Fib( int north)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0;
if (n == 0) return a;
for ( int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
public static void Main( string [] args)
{
int n = 9;
Panel.Write( "{0} " , Fib(due north));
}
}
}
PHP
<?php
function fib( $n )
{
$a = 0;
$b = 1;
$c ;
$i ;
if ( $north == 0)
return $a ;
for ( $i = 2; $i <= $northward ; $i ++)
{
$c = $a + $b ;
$a = $b ;
$b = $c ;
}
render $b ;
}
$north = 9;
echo fib( $north );
?>
Javascript
<script>
function fib(n)
{
let a = 0, b = i, c, i;
if ( n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
permit n = 9;
certificate.write(fib(n));
</script>
Fourth dimension Complexity: O(n)
Actress Space: O(ane)
Method 4: Using power of the matrix {{one, one}, {1, 0}}
This is some other O(n) that relies on the fact that if we n times multiply the matrix M = {{1,1},{1,0}} to itself (in other words calculate power(M, n)), and then we become the (n+1)th Fibonacci number as the element at row and cavalcade (0, 0) in the resultant matrix.
The matrix representation gives the following closed expression for the Fibonacci numbers:
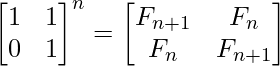
C++
#include<$.25/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void multiply( int F[two][2], int M[two][2]);
void power( int F[ii][2], int due north);
int fib( int due north)
{
int F[ii][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { one, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
render 0;
power(F, north - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply( int F[2][2], int K[2][2])
{
int ten = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][ane] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[i][1];
int z = F[ane][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[ane][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][one] * Chiliad[1][1];
F[0][0] = 10;
F[0][i] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][i] = westward;
}
void power( int F[two][two], int northward)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, i }, { 1, 0 } };
for (i = 2; i <= northward; i++)
multiply(F, 1000);
}
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << " " << fib(n);
return 0;
}
C
#include <stdio.h>
void multiply( int F[2][ii], int M[two][two]);
void power( int F[two][ii], int n);
int fib( int n)
{
int F[two][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
ability(F, due north-1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply( int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*K[0][0] + F[0][i]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][one] + F[0][1]*Thou[1][ane];
int z = F[ane][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*Thousand[1][0];
int west = F[1][0]*Grand[0][1] + F[i][ane]*Yard[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][one] = w;
}
void power( int F[2][two], int n)
{
int i;
int M[two][2] = {{i,1},{1,0}};
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, K);
}
int main()
{
int n = ix;
printf ( "%d" , fib(n));
getchar ();
return 0;
}
Java
public class fibonacci
{
static int fib( int n)
{
int F[][] = new int [][]{{ 1 , 1 },{ 1 , 0 }};
if (north == 0 )
return 0 ;
power(F, n- 1 );
return F[ 0 ][ 0 ];
}
static void multiply( int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[ 0 ][ 0 ]*M[ 0 ][ 0 ] + F[ 0 ][ ane ]*M[ one ][ 0 ];
int y = F[ 0 ][ 0 ]*M[ 0 ][ 1 ] + F[ 0 ][ 1 ]*M[ 1 ][ 1 ];
int z = F[ one ][ 0 ]*1000[ 0 ][ 0 ] + F[ 1 ][ one ]*Thou[ ane ][ 0 ];
int w = F[ 1 ][ 0 ]*M[ 0 ][ one ] + F[ 1 ][ 1 ]*Thousand[ one ][ 1 ];
F[ 0 ][ 0 ] = ten;
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] = y;
F[ i ][ 0 ] = z;
F[ ane ][ 1 ] = w;
}
static void ability( int F[][], int northward)
{
int i;
int M[][] = new int [][]{{ ane , 1 },{ 1 , 0 }};
for (i = 2 ; i <= north; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = ix ;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
};
Python3
def fib(n):
F = [[ 1 , one ],
[ 1 , 0 ]]
if (n = = 0 ):
return 0
ability(F, due north - 1 )
return F[ 0 ][ 0 ]
def multiply(F, M):
10 = (F[ 0 ][ 0 ] * Grand[ 0 ][ 0 ] +
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] * Chiliad[ ane ][ 0 ])
y = (F[ 0 ][ 0 ] * Thousand[ 0 ][ ane ] +
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] * One thousand[ ane ][ one ])
z = (F[ one ][ 0 ] * M[ 0 ][ 0 ] +
F[ 1 ][ 1 ] * M[ ane ][ 0 ])
west = (F[ 1 ][ 0 ] * M[ 0 ][ 1 ] +
F[ i ][ ane ] * M[ one ][ ane ])
F[ 0 ][ 0 ] = ten
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] = y
F[ i ][ 0 ] = z
F[ i ][ ane ] = westward
def power(F, n):
M = [[ i , 1 ],
[ 1 , 0 ]]
for i in range ( 2 , n + 1 ):
multiply(F, Grand)
if __name__ = = "__main__" :
n = nine
impress (fib(n))
C#
using Arrangement;
class GFG {
static int fib( int n)
{
int [,]F = new int [,] {{1, one},
{1, 0} };
if (northward == 0)
return 0;
power(F, due north-one);
return F[0,0];
}
static void multiply( int [,]F, int [,]G)
{
int x = F[0,0]*Chiliad[0,0] + F[0,1]*M[1,0];
int y = F[0,0]*One thousand[0,1] + F[0,one]*M[1,1];
int z = F[1,0]*M[0,0] + F[1,ane]*M[ane,0];
int w = F[1,0]*Grand[0,i] + F[1,one]*M[1,i];
F[0,0] = x;
F[0,i] = y;
F[1,0] = z;
F[i,1] = w;
}
static void power( int [,]F, int due north)
{
int i;
int [,]Thou = new int [,]{{i, 1},
{1, 0} };
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, Chiliad);
}
public static void Main ()
{
int n = nine;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
PHP
<?php
function fib( $due north )
{
$F = array ( array (1, 1),
array (i, 0));
if ( $n == 0)
render 0;
power( $F , $n - 1);
return $F [0][0];
}
function multiply(& $F , & $1000 )
{
$x = $F [0][0] * $Chiliad [0][0] +
$F [0][1] * $M [1][0];
$y = $F [0][0] * $G [0][1] +
$F [0][ane] * $Yard [one][1];
$z = $F [ane][0] * $M [0][0] +
$F [i][ane] * $M [1][0];
$w = $F [1][0] * $Yard [0][1] +
$F [1][1] * $Grand [1][ane];
$F [0][0] = $10 ;
$F [0][1] = $y ;
$F [1][0] = $z ;
$F [ane][1] = $westward ;
}
function power(& $F , $north )
{
$M = array ( array (one, 1),
array (1, 0));
for ( $i = 2; $i <= $north ; $i ++)
multiply( $F , $M );
}
$n = 9;
echo fib( $n );
?>
Javascript
<script>
function fib( n)
{
var F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ];
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - one);
return F[0][0];
}
office multiply( F, Thou )
{
ten = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * K[1][0];
y = F[0][0] * 1000[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[i][1];
z = F[i][0] * M[0][0] +
F[one][1] * M[i][0];
westward = F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[i][i] * G[i][ane];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][i] = y;
F[i][0] = z;
F[1][1] = westward;
}
function power( F, northward)
{
var i;
var M = [[ 1, ane ], [ 1, 0 ]];
for (i = ii; i <= north; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
var n = 9;
document.write ( " " + fib(n));
</script>
Time Complexity: O(n)
Actress Infinite: O(1)
Method 5: (Optimized Method 4)
Method 4 can be optimized to work in O(Logn) fourth dimension complexity. We tin can do recursive multiplication to go power(M, north) in the previous method (Similar to the optimization washed in this post)
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void multiply( int F[2][two], int 1000[2][ii]);
void ability( int F[ii][2], int n);
int fib( int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1, one}, {i, 0}};
if (northward == 0)
return 0;
power(F, north - 1);
render F[0][0];
}
void ability( int F[2][2], int n)
{
if (due north == 0 || northward == 1)
return ;
int One thousand[2][2] = {{1, i}, {one, 0}};
power(F, northward / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (northward % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply( int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int 10 = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][ane] * M[i][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][one] + F[0][ane] * M[1][one];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[i][0];
int westward = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][one] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[i][1] = westward;
}
int master()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(nine);
getchar ();
return 0;
}
C
#include <stdio.h>
void multiply( int F[2][2], int G[2][2]);
void power( int F[2][2], int n);
int fib( int n)
{
int F[ii][ii] = {{1,one},{ane,0}};
if (n == 0)
render 0;
power(F, n-i);
return F[0][0];
}
void ability( int F[2][ii], int n)
{
if ( north == 0 || n == 1)
return ;
int Thousand[two][2] = {{1,one},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, Grand);
}
void multiply( int F[2][2], int Chiliad[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][i] + F[0][1]*M[1][i];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[ane][ane]*Chiliad[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*G[0][1] + F[ane][1]*M[ane][1];
F[0][0] = ten;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf ( "%d" , fib(9));
getchar ();
return 0;
}
Java
public form fibonacci
{
static int fib( int north)
{
int F[][] = new int [][]{{ one , 1 },{ 1 , 0 }};
if (n == 0 )
render 0 ;
power(F, n- i );
return F[ 0 ][ 0 ];
}
static void multiply( int F[][], int One thousand[][])
{
int x = F[ 0 ][ 0 ]*M[ 0 ][ 0 ] + F[ 0 ][ ane ]*Thou[ one ][ 0 ];
int y = F[ 0 ][ 0 ]*Grand[ 0 ][ 1 ] + F[ 0 ][ i ]*Yard[ 1 ][ 1 ];
int z = F[ 1 ][ 0 ]*Thousand[ 0 ][ 0 ] + F[ i ][ 1 ]*K[ 1 ][ 0 ];
int w = F[ 1 ][ 0 ]*Thousand[ 0 ][ one ] + F[ 1 ][ 1 ]*M[ 1 ][ i ];
F[ 0 ][ 0 ] = x;
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] = y;
F[ one ][ 0 ] = z;
F[ 1 ][ 1 ] = w;
}
static void power( int F[][], int northward)
{
if ( due north == 0 || n == i )
render ;
int Yard[][] = new int [][]{{ i , ane },{ ane , 0 }};
power(F, n/ two );
multiply(F, F);
if (northward% ii != 0 )
multiply(F, M);
}
public static void chief (String args[])
{
int n = 9 ;
System.out.println(fib(north));
}
};
Python3
def fib(n):
F = [[ i , one ],
[ i , 0 ]]
if (n = = 0 ):
return 0
power(F, n - 1 )
return F[ 0 ][ 0 ]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[ 0 ][ 0 ] * G[ 0 ][ 0 ] +
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] * Thou[ 1 ][ 0 ])
y = (F[ 0 ][ 0 ] * One thousand[ 0 ][ 1 ] +
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] * M[ 1 ][ 1 ])
z = (F[ i ][ 0 ] * M[ 0 ][ 0 ] +
F[ 1 ][ 1 ] * M[ 1 ][ 0 ])
w = (F[ 1 ][ 0 ] * Thou[ 0 ][ 1 ] +
F[ ane ][ 1 ] * M[ 1 ][ 1 ])
F[ 0 ][ 0 ] = 10
F[ 0 ][ 1 ] = y
F[ i ][ 0 ] = z
F[ 1 ][ i ] = w
def ability(F, due north):
if ( northward = = 0 or northward = = 1 ):
return ;
M = [[ 1 , ane ],
[ i , 0 ]];
power(F, n / / 2 )
multiply(F, F)
if (n % two ! = 0 ):
multiply(F, 1000)
if __name__ = = "__main__" :
n = 9
print (fib(n))
C#
using System;
course GFG
{
static int fib( int n)
{
int [,] F = new int [,]{{i, i},
{1, 0}};
if (due north == 0)
return 0;
power(F, north - i);
return F[0, 0];
}
static void multiply( int [,] F,
int [,] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * G[0, 0] +
F[0, 1] * M[ane, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, ane] +
F[0, 1] * Grand[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * G[0, 0] +
F[1, 1] * Yard[1, 0];
int west = F[i, 0] * Thou[0, ane] +
F[1, 1] * M[one, ane];
F[0, 0] = ten;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[i, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = due west;
}
static void power( int [,] F, int n)
{
if ( n == 0 || due north == 1)
return ;
int [,] K = new int [,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
power(F, n / ii);
multiply(F, F);
if (north % two != 0)
multiply(F, Thousand);
}
public static void Main ()
{
int north = 9;
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
Javascript
<script>
part fib(northward)
{
var F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ];
if (northward == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
render F[0][0];
}
function multiply(F, Grand)
{
var x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[ane][0];
var y = F[0][0] * One thousand[0][one] + F[0][1] * Chiliad[i][1];
var z = F[1][0] * G[0][0] + F[i][i] * M[1][0];
var w = F[one][0] * Chiliad[0][1] + F[1][1] * One thousand[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
function power(F, due north)
{
if (north == 0 || n == 1)
return ;
var M = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ i, 0 ] ];
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (northward % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
var n = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
</script>
Fourth dimension Complexity: O(Logn)
Extra Space: O(Logn) if nosotros consider the role call stack size, otherwise O(1).
Method 6: (O(Log n) Fourth dimension)
Below is one more than interesting recurrence formula that can be used to detect n'th Fibonacci Number in O(Log n) time.
If due north is even then k = n/ii: F(northward) = [ii*F(k-1) + F(k)]*F(yard) If n is odd then k = (n + 1)/2 F(n) = F(k)*F(thousand) + F(k-ane)*F(g-one)
How does this formula piece of work?
The formula can be derived from the above matrix equation.
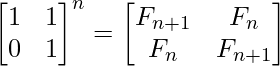
Taking determinant on both sides, nosotros get (-1)n = Fdue north+oneFdue north-1 - Fnorth ii Moreover, since AnAm = An+one thousand for any square matrix A, the following identities tin can be derived (they are obtained from two dissimilar coefficients of the matrix product) FyardFn + Fchiliad-oneFn-1 = Fg+n-ane ---------------------------(i) By putting n = n+1 in equation(1), FmFnorthward+ane + Fm-1Fn = Fm+n --------------------------(2) Putting 1000 = n in equation(i). F2n-1 = Fn 2 + Fnorth-1 two Putting m = due north in equation(ii) F2n = (Fn-i + Fn+1)Fdue north = (2Fn-1 + Fn)Fn (Source: Wiki) -------- ( Past putting Fn+1 = Fn + Fn-1 ) To get the formula to exist proved, nosotros simply need to practice the following If northward is even, we tin can put k = n/ii If n is odd, we can put m = (north+i)/ii
Below is the implementation of the higher up thought.
C++
#include <$.25/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = chiliad;
int f[MAX] = {0};
int fib( int north)
{
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || northward == 2)
return (f[north] = 1);
if (f[n])
render f[n];
int thou = (n & 1)? (n+1)/ii : n/ii;
f[due north] = (n & 1)? (fib(1000)*fib(k) + fib(g-ane)*fib(k-1))
: (2*fib(grand-i) + fib(k))*fib(k);
return f[n];
}
int main()
{
int due north = ix;
printf ( "%d " , fib(n));
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
static int MAX = m ;
static int f[];
public static int fib( int due north)
{
if (north == 0 )
return 0 ;
if (n == 1 || north == 2 )
return (f[n] = i );
if (f[n] != 0 )
return f[northward];
int k = (north & 1 ) == one ? (n + 1 ) / 2
: due north / ii ;
f[n] = (due north & 1 ) == 1 ? (fib(k) * fib(thou) +
fib(m - one ) * fib(one thousand - one ))
: ( 2 * fib(k - one ) + fib(k))
* fib(k);
return f[north];
}
public static void primary(String[] args)
{
int n = nine ;
f= new int [MAX];
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
};
Python3
MAX = 1000
f = [ 0 ] * MAX
def fib(n) :
if (n = = 0 ) :
render 0
if (northward = = 1 or northward = = 2 ) :
f[northward] = 1
return (f[n])
if (f[n]) :
return f[n]
if ( n & one ) :
1000 = (due north + one ) / / ii
else :
k = n / / 2
if ((n & 1 ) ) :
f[n] = (fib(yard) * fib(k) + fib(thou - 1 ) * fib(k - 1 ))
else :
f[northward] = ( ii * fib(thou - i ) + fib(g)) * fib(k)
return f[n]
n = nine
print (fib(n))
C#
using Organization;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = m;
static int [] f;
public static int fib( int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == ane || n == ii)
return (f[due north] = 1);
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & ane) == i ? (north + 1) / two
: n / 2;
f[n] = (north & 1) == 1 ? (fib(k) * fib(chiliad) +
fib(g - 1) * fib(grand - one))
: (2 * fib(thou - i) + fib(k)) *
fib(k);
render f[due north];
}
static void Primary()
{
int n = 9;
f = new int [MAX];
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
PHP
<?php
$MAX = grand;
function fib( $n )
{
global $MAX ;
$f = array_fill (0, $MAX , Nada);
if ( $north == 0)
return 0;
if ( $due north == i || $n == 2)
return ( $f [ $n ] = 1);
if ( $f [ $n ])
return $f [ $n ];
$k = ( $n & one) ? ( $n + ane) / ii : $n / 2;
$f [ $n ] = ( $n & 1) ? (fib( $k ) * fib( $k ) +
fib( $one thousand - 1) * fib( $g - 1)) :
(2 * fib( $k - 1) + fib( $k )) * fib( $yard );
return $f [ $n ];
}
$northward = 9;
echo fib( $northward );
?>
Javascript
<script>
const MAX = m;
var f = [...Array(MAX)];
f.fill(0);
role fib(northward) {
if (northward == 0) return 0;
if (north == 1 || n == 2) return (f[northward] = ane);
if (f[north]) return f[n];
var k = n & i ? (northward + ane) / 2 : n / 2;
f[north] =
due north & i
? fib(thou) * fib(g) + fib(1000 - 1) * fib(g - 1)
: (2 * fib(m - 1) + fib(k)) * fib(k);
return f[n];
}
var n = 9;
document.write(fib(northward));
</script>
Fourth dimension complexity: O(Log n), as we divide the trouble in one-half in every recursive call.
Method vii: (Another arroyo(Using Binet's formula))
In this method, we directly implement the formula for the nth term in the Fibonacci series.
Fn = {[(√v + 1)/2] ^ due north} / √five
Note: Above Formula gives correct result only upto for northward<71. Considering as nosotros motion frontward from n>=71 , rounding error becomes significantly large . Although , using floor function instead of round function will give right issue for n=71 . Only afterwards from n=72 , it also fails.
Example: For N=72 , Right result is 498454011879264 but above formula gives 498454011879265.
Reference: http://www.maths.surrey.ac.uk/hosted-sites/R.Knott/Fibonacci/fibFormula.html
C++
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
int fib( int northward) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt (5)) / 2;
return circular( prisoner of war (phi, n) / sqrt (5));
}
int main ()
{
int n = ix;
std::cout << fib(n) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int fib( int due north) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt (5)) / 2;
render circular( pow (phi, n) / sqrt (5));
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf ( "%d" , fib(n));
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
static int fib( int n)
{
double phi = ( 1 + Math.sqrt( 5 )) / 2 ;
return ( int )Math.round(Math.pow(phi, northward)
/ Math.sqrt( five ));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9 ;
Arrangement.out.println(fib(due north));
}
};
Python3
import math
def fibo(due north):
phi = ( 1 + math.sqrt( five )) / 2
return circular ( pow (phi, n) / math.sqrt( 5 ))
if __name__ = = '__main__' :
n = 9
print (fibo(northward))
C#
using System;
public grade GFG
{
static int fib( int n)
{
double phi = (1 + Math.Sqrt(5)) / 2;
render ( int ) Math.Circular(Math.Pow(phi, n)
/ Math.Sqrt(5));
}
public static void Chief()
{
int due north = nine;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
PHP
<?php
part fib( $n )
{
$phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return circular (pow( $phi , $due north ) / sqrt(five));
}
$n = 9;
echo fib( $north ) ;
?>
Javascript
<script>
function fib(due north) {
let phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return Math.round(Math.pw(phi, n) / Math.sqrt(5));
}
allow northward = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
</script>
Fourth dimension Complication : O(logn), this is considering computing phi^n takes logn time
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Method 8: DP using memoization(Top down approach)
We tin can avoid the repeated work washed in method ane past storing the Fibonacci numbers calculated so far. We only need to store all the values in an array.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[x];
int fib( int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
int commencement, 2nd;
if (dp[north - i] != -1)
showtime = dp[n - ane];
else
outset = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - ii] != -1)
second = dp[n - two];
else
2nd = fib(due north - 2);
return dp[due north] = outset + second;
}
int master()
{
int n = 9;
memset (dp, -1, sizeof (dp));
cout << fib(n);
getchar ();
return 0;
}
Coffee
import coffee.util.*;
public course GFG {
static int [] dp = new int [ 10 ];
static int fib( int n)
{
if (n <= one )
return n;
int first, second;
if (dp[northward - 1 ] != - 1 )
beginning = dp[n - 1 ];
else
commencement = fib(n - one );
if (dp[due north - two ] != - 1 )
second = dp[north - ii ];
else
2d = fib(n - 2 );
return dp[n] = first + 2nd;
}
public static void primary(String[] args)
{
int n = nine ;
Arrays.fill(dp, - 1 );
Organization.out.print(fib(north));
}
};
Python3
dp = [ - 1 for i in range ( 10 )]
def fib(north):
if (due north < = 1 ):
return due north;
global dp;
get-go = 0 ;
second = 0 ;
if (dp[north - 1 ] ! = - i ):
beginning = dp[n - 1 ];
else :
first = fib(n - ane );
if (dp[north - 2 ] ! = - one ):
2nd = dp[north - 2 ];
else :
second = fib(due north - two );
dp[northward] = first + second;
return dp[n] ;
if __name__ = = '__main__' :
n = 9 ;
print (fib(n));
C#
using Organisation;
grade GFG {
static int [] dp = new int [10];
static int fib( int n)
{
if (north <= 1)
return due north;
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[northward - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - two] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
2d = fib(northward - 2);
return dp[north] = beginning + 2nd;
}
static void Chief()
{
int n = 9;
Array.Make full(dp, -i);
Console.Write(fib(north));
}
}
Javascript
<script>
dp = Array.from({length: 10}, (_, i) => -1);
function fib(northward)
{
if (n <= one)
render north;
var first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - one];
else
kickoff = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[north - 2];
else
second = fib(due north - 2);
return dp[n] = first + 2nd;
}
var n = 9;
certificate.write(fib(n));
</script>
Related Articles:
Big Fibonacci Numbers in Coffee
Please write comments if you discover the above codes/algorithms wrong, or find other means to solve the aforementioned trouble.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number
http://www.ics.uci.edu/~eppstein/161/960109.html
5 8 13 21 34,
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/program-for-nth-fibonacci-number/
Posted by: walkupthoon1994.blogspot.com


0 Response to "5 8 13 21 34"
Post a Comment